Sentiment Analysis with Bag of Words and a Multilayer Perceptron
Use TF Keras to build and test various MLPs on Movie Sentiment Analysis. Use NLTK to clean data.
Part 1: clean text data, generate vocabulary, transform data
Part 2: build various MLP models (1 hidden layer, 2 hidden layers)
Part 3: build testing harness
Part 4: test various MLP models and encoding schemes
Part 5: test on two real reviews
Win condition: >87% accuracy on test split (87% is the upper bound for SVM and other traditional ML techniques on this data, see: http://www.cs.cornell.edu/home/llee/papers/pang-lee-stars.pdf
Attributions: machinelearningmastery.com DL for NLP book
polarity dataset v2.0 ( 3.0Mb) (includes README v2.0): 1000 positive and 1000 negative processed reviews. Introduced in Pang/Lee ACL 2004. Released June 2004.
Import Libraries
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from collections import Counter
from os import listdir
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
from tensorflow.keras.utils import plot_model
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import datetime
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import tensorflow.keras as tk
%load_ext tensorboard
The tensorboard extension is already loaded. To reload it, use:
%reload_ext tensorboard
Data Engineering
root_dir = 'review_polarity/txt_sentoken/'
neg_train_dir = root_dir + 'neg_train'
neg_test_dir = root_dir + 'neg_test'
pos_train_dir = root_dir + 'pos_train'
pos_test_dir = root_dir + 'pos_test'
Data cleaning function
def load_doc(filename):
file = open(filename, 'r')
text = file.read()
file.close()
return text
def clean_doc(text):
words = nltk.word_tokenize(text)
alpha_words = [w for w in words if w.isalpha()]
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('english'))
relevant_words = [w for w in alpha_words if w not in stop_words]
filtered_words = [w for w in relevant_words if len(w)>1]
return filtered_words
Build a vocabulary with the training data
def add_doc_to_vocab(filename, vocab):
doc = load_doc(filename)
tokens = clean_doc(doc)
vocab.update(tokens)
def process_docs_to_vocab(directory, vocab):
i=0
for filename in listdir(directory):
if filename.startswith('cv'):
path = directory + '/' + filename
add_doc_to_vocab(path, vocab)
i+=1
print(f'Processed {i} docs.')
return vocab
vocab = Counter()
process_docs_to_vocab(pos_train_dir, vocab)
process_docs_to_vocab(neg_train_dir, vocab)
print(len(vocab))
Processed 900 docs.
Processed 900 docs.
36388
print(vocab.most_common(25))
[('film', 8513), ('movie', 5032), ('one', 5002), ('like', 3196), ('even', 2262), ('good', 2076), ('time', 2041), ('would', 2037), ('story', 1932), ('much', 1825), ('character', 1783), ('also', 1757), ('get', 1728), ('characters', 1655), ('two', 1645), ('first', 1588), ('see', 1558), ('way', 1516), ('well', 1479), ('could', 1444), ('make', 1420), ('really', 1400), ('little', 1350), ('films', 1345), ('life', 1343)]
def filter_vocab(vocab, min_occurrences=5):
tokens = [k for k, c in vocab.items() if c >= min_occurrences]
print(len(tokens))
return tokens
filtered_vocab = filter_vocab(vocab, 2)
23548
def save_list(tokens, filename):
if type(tokens[0]) != str:
tokens = str(tokens)
data = '\n'.join(tokens)
file = open(filename, 'w')
file.write(data)
file.close()
save_list(filtered_vocab, 'vocab.txt')
Now user our vocabulary to process our data
vocab_set = set(load_doc('vocab.txt').split())
print(len(vocab_set))
23548
def doc_to_line(filename, vocab):
doc = load_doc(filename)
tokens = clean_doc(doc)
vocab_tokens = [w for w in tokens if w in vocab_set]
return ' '.join(vocab_tokens)
def process_docs_to_lines(directory, vocab):
lines = list()
for filename in listdir(directory):
if filename.startswith('cv'):
path = directory + '/' + filename
line = doc_to_line(path, vocab)
lines.append(line)
return lines
neg_train = process_docs_to_lines(neg_train_dir, vocab_set)
pos_train = process_docs_to_lines(pos_train_dir, vocab_set)
neg_test = process_docs_to_lines(neg_test_dir, vocab_set)
pos_test = process_docs_to_lines(pos_test_dir, vocab_set)
trainX, trainY = neg_train+pos_train, [0]*len(neg_train)+[1]*len(pos_train)
testX, testY = neg_test+pos_test, [0]*len(neg_test)+[1]*len(pos_test)
print(len(trainX), len(trainY))
print(len(testX), len(testY))
1800 1800
200 200
save_list(trainX, 'trainX.txt')
save_list(trainY, 'trainY.txt')
save_list(testX, 'testX.txt')
save_list(testY, 'testY.txt')
Transform data to prepare for modelling, using BOW representation
processed_data = {}
processed_data['trainX'] = trainX
processed_data['trainY'] = trainY
processed_data['testX'] = testX
processed_data['testY'] = testY
tokenizer = Tokenizer()
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(trainX)
def gen_encodings(X, tokenizer):
output={}
modes = ['binary', 'count', 'tfidf', 'freq']
for mode in modes:
output[mode] = tokenizer.texts_to_matrix(X, mode=mode)
return output
trainX_dict, testX_dict = gen_encodings(processed_data['trainX'], tokenizer), gen_encodings(processed_data['testX'], tokenizer)
print(trainX_dict['binary'][:10])
[[0. 1. 1. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 1. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 1. ... 0. 0. 0.]
...
[0. 1. 1. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 1. ... 0. 0. 0.]]
Build Models
input_vec_len = trainX_dict['binary'].shape[1]
mlp1 = Sequential(name='mlp1')
mlp1.add(Dense(50, input_shape=(input_vec_len, ), activation='relu'))
mlp1.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
mlp1.summary()
plot_model(mlp1)
Model: "mlp1"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense_11 (Dense) (None, 50) 1177500
_________________________________________________________________
dense_12 (Dense) (None, 1) 51
=================================================================
Total params: 1,177,551
Trainable params: 1,177,551
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
mlp2 = Sequential(name='mlp2')
mlp2.add(Dense(25, input_shape=(input_vec_len,), activation='relu'))
mlp2.add(Dense(25, activation='relu'))
mlp2.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
mlp2.summary()
plot_model(mlp2)
Model: "mlp2"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense_13 (Dense) (None, 25) 588750
_________________________________________________________________
dense_14 (Dense) (None, 25) 650
_________________________________________________________________
dense_15 (Dense) (None, 1) 26
=================================================================
Total params: 589,426
Trainable params: 589,426
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
Build a Testing Harness
def gen_model(name, input_vec_len):
if name == 'mlp1':
model = Sequential(name='mlp1')
model.add(Dense(50, input_shape=(input_vec_len, ), activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
if name =='mlp2':
model = Sequential(name='mlp2')
model.add(Dense(25, input_shape=(input_vec_len,), activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(25, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
def evaluate_model(model_name, data, n_repeats=5):
trainX, trainY, testX, testY = data
scores = []
# create tensorboard callback
log_dir = 'logs/fit/' + datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d-%H%M%S')
tb_callback = tk.callbacks.TensorBoard(log_dir=log_dir, histogram_freq=1)
for i in range(n_repeats):
model = gen_model(model_name, trainX.shape[1])
H = model.fit(trainX, trainY,
validation_data=(testX, testY),
epochs=10,
callbacks=[tb_callback],
verbose=2)
scores.append(H.history['val_accuracy'])
return scores
models = ['mlp1', 'mlp2']
trainY = np.array(trainY)
testY = np.array(testY)
results = pd.DataFrame()
for model_name in models:
for mode in trainX_dict.keys():
data = trainX_dict[mode], trainY, testX_dict[mode], testY
results[model_name,'and',mode] = evaluate_model(model_name, data)
Train on 1800 samples, validate on 200 samples
Epoch 1/10
1800/1800 - 5s - loss: 0.4730 - accuracy: 0.7856 - val_loss: 0.2800 - val_accuracy: 0.9150
Epoch 2/10
1800/1800 - 2s - loss: 0.0608 - accuracy: 0.9944 - val_loss: 0.2422 - val_accuracy: 0.9200
Epoch 3/10
1800/1800 - 2s - loss: 0.0175 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 0.2269 - val_accuracy: 0.9100
...
Epoch 9/10
1800/1800 - 2s - loss: 0.1537 - accuracy: 0.9917 - val_loss: 0.3455 - val_accuracy: 0.8800
Epoch 10/10
1800/1800 - 2s - loss: 0.1140 - accuracy: 0.9961 - val_loss: 0.3204 - val_accuracy: 0.9100
results_unraveled = pd.DataFrame()
for index, column in results.T.iterrows():
results_unraveled[index] = [e for l in column for e in l]
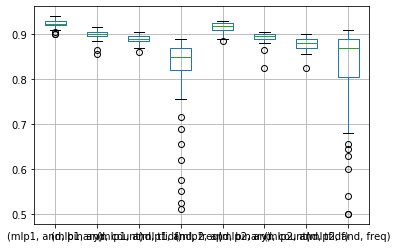
results_unraveled.describe()
| (mlp1, and, binary) | (mlp1, and, count) | (mlp1, and, tfidf) | (mlp1, and, freq) | (mlp2, and, binary) | (mlp2, and, count) | (mlp2, and, tfidf) | (mlp2, and, freq) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 50.000000 | 50.000000 | 50.000000 | 50.000000 | 50.000000 | 50.000000 | 50.000000 | 50.000000 |
| mean | 0.922500 | 0.897400 | 0.889300 | 0.811600 | 0.916100 | 0.893300 | 0.878900 | 0.820100 |
| std | 0.008097 | 0.010412 | 0.010051 | 0.099747 | 0.011079 | 0.013117 | 0.015396 | 0.111746 |
| min | 0.900000 | 0.855000 | 0.860000 | 0.510000 | 0.885000 | 0.825000 | 0.825000 | 0.500000 |
| 25% | 0.920000 | 0.895000 | 0.885000 | 0.821250 | 0.910000 | 0.890000 | 0.870000 | 0.803750 |
| 50% | 0.922500 | 0.900000 | 0.890000 | 0.850000 | 0.917500 | 0.895000 | 0.880000 | 0.870000 |
| 75% | 0.930000 | 0.905000 | 0.895000 | 0.870000 | 0.925000 | 0.900000 | 0.890000 | 0.890000 |
| max | 0.940000 | 0.915000 | 0.905000 | 0.890000 | 0.930000 | 0.905000 | 0.900000 | 0.910000 |
results_unraveled.boxplot()
plt.show()
Test against two real reviews
The best model was the wider model, and the best encoding method was the binary encoding. Let’s test it against two real reviews.
model = gen_model('mlp1', trainX_dict['binary'].shape[1])
# create tensorboard callback
log_dir = 'logs/fit/' + datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d-%H%M%S')
tb_callback = tk.callbacks.TensorBoard(log_dir=log_dir, histogram_freq=1)
H = model.fit(trainX_dict['binary'], trainY,
epochs=10,
callbacks=[tb_callback],
verbose=0)
def pos_or_neg(filename, vocab_set, model, tokenizer):
test = []
test.append(doc_to_line(filename, vocab_set))
test = tokenizer.texts_to_matrix(test)
p = model.predict(test)[0][0]
if round(p) == 0:
print('This was a negative review with probability:', round((1-p)*100,2),'%')
elif round(p) == 1:
print('This was a positive review with probability:', round((p)*100,2),'%')
The first test is a negative review of the new star wars movie, giving it 1/5 stars.
pos_or_neg('negative_star_wars_review.txt', vocab_set, model, tokenizer)
This was a negative review with probability: 81.43 %
The second test is a positive review of the new star wars moving giving it 3.5/4 stars.
pos_or_neg('positive_star_wars_review.txt', vocab_set, model, tokenizer)
This was a positive review with probability: 99.41 %
Pretty cool, it guesses right with reasonably high confidence on both reviews!